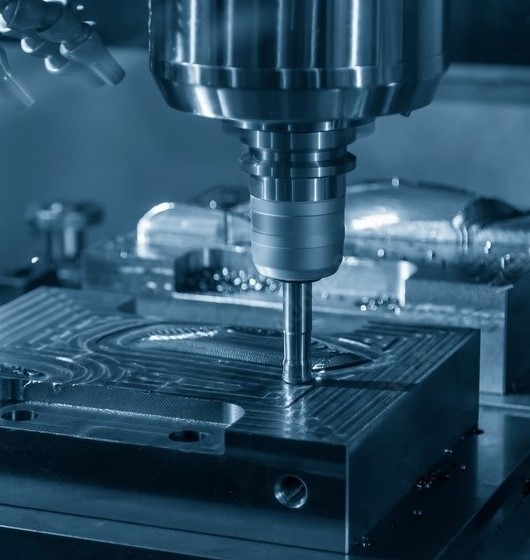

CNC Milling
Advanced CNC milling technology with up to 4-axis capabilities
Superior surface finishes with CNC milling, achieving roughness values as low as 0.4 μm Ra


Advanced CNC milling technology with up to 4-axis capabilities
Superior surface finishes with CNC milling, achieving roughness values as low as 0.4 μm Ra
Rollmec excels in CNC milling with advanced multi-axis capabilities, achieving intricate geometries with tight tolerances
Our top notch machining facilities ensure dimensional accuracy within microns, meeting standard tolerances (ISO 2768) or as per the drawings. With a production capacity of over 100k parts per month, we handle projects of all sizes. Our expertise spans various materials, and our skilled engineers optimize cutting parameters and tool paths for optimal efficiency. From rapid prototyping to large-scale production, our CNC milling delivers precise results, blending technology and craftsmanship seamlessly.
Rollmec excels in 3-axis milling, a fundamental CNC milling technique. In 3-axis milling, the milling machine moves along the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for precise cuts and shaping of materials. This capability enables Rollmec to produce components with a wide range of geometries, from simple to moderately complex. The 3-axis milling process involves securing the workpiece and positioning it accurately on the machine bed. The cutting tool, typically an end mill, removes material by moving along the three axes. This versatile technique is ideal for creating flat surfaces, slots, holes, and contours, and is widely used in various industries.
Rollmec’s expertise extends to 4-axis milling, which adds rotational movement to the capabilities of 3-axis milling. In addition to the X, Y, and Z axes, the 4-axis milling machine features a rotary axis, usually referred to as the A-axis. This additional axis allows for the rotation of the workpiece, enabling the milling tool to access different angles and contours. The A-axis rotation is typically used for creating features like holes, threads, and curved surfaces. With 4-axis milling, Rollmec can efficiently machine more complex components that require intricate features and contours from multiple angles.
Rollmec’s advanced manufacturing capabilities include vertical milling center ( 5-axis milling) (Continuous and Indexed), a highly versatile and precise milling technique. With 5-axis milling, the machine’s cutting tool can move along all three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) while simultaneously rotating on two additional rotational axes, typically referred to as the A and B axes. This multidirectional movement allows for the creation of complex and intricate geometries with exceptional accuracy. 5-axis milling is particularly valuable for machining components that require undercuts, deep cavities, or complex surface contours. By eliminating the need for multiple setups, 5-axis milling reduces production time, increases efficiency, and ensures superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Rollmec’s proficiency in 5-axis milling enables the precise fabrication of intricate components for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
CNC milling machines come in various types, and while 3-axis and 3+2 axis machines are ideal for parts with simpler geometries, 4-axis and 5-axis machines offer enhanced capabilities for machining intricate and complex components.
| Application | Maximum Part Size (Metric) | Maximum Part Size (Imperial) |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Metal | 500mm x 300mm x 200mm | 19.69" x 11.81" x 7.87" |
| Soft Metal | 600mm x 400mm x 250mm | 23.62" x 15.75" x 9.84" |
| Minimum Features | 0.2mm | 0.008" |
| Application | Maximum Part Size (Metric) | Maximum Part Size (Imperial) |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Metal | 500 mm x 500 mm x 400 mm | 19.7" x 19.7" x 15.7" |
| Soft Metal | 600 mm x 600 mm x 300 mm | 23.6" x 23.6" x 11.8" |
| Minimum Features | 0.2 mm | 0.008" |
As the epitome of machining technology, 5-axis milling machines offer unparalleled capabilities for producing intricate parts with complex geometries, resulting in increased productivity due to reduced setup requirements
| Application | Hard Metal (mm) | Hard Metal (inches) | Soft Metal (mm) | Soft Metal (inches) | Minimum Features (mm) | Minimum Features (inches) |
| Aerospace | 800 x 800 x 600 | 31.5 x 31.5 x 23.6 | 1000 x 1000 x 800 | 39.4 x 39.4 x 31.5 | 0.1 | 0.004 |
| Automotive | 600 x 400 x 400 | 23.6 x 15.7 x 15.7 | 800 x 600 x 500 | 31.5 x 23.6 x 19.7 | 0.05 | 0.002 |
| Medical Devices | 300 x 300 x 200 | 11.8 x 11.8 x 7.9 | 400 x 400 x 300 | 15.7 x 15.7 x 11.8 | 0.05 | 0.002 |
| Electronics | 400 x 300 x 200 | 15.7 x 11.8 x 7.9 | 600 x 400 x 300 | 23.6 x 15.7 x 11.8 | 0.05 | 0.002 |
| Prototyping | 500 x 500 x 400 | 19.7 x 19.7 x 15.7 | 800 x 800 x 600 | 31.5 x 31.5 x 23.6 | 0.1 | 0.004 |
Custom solutions for industries around the globe
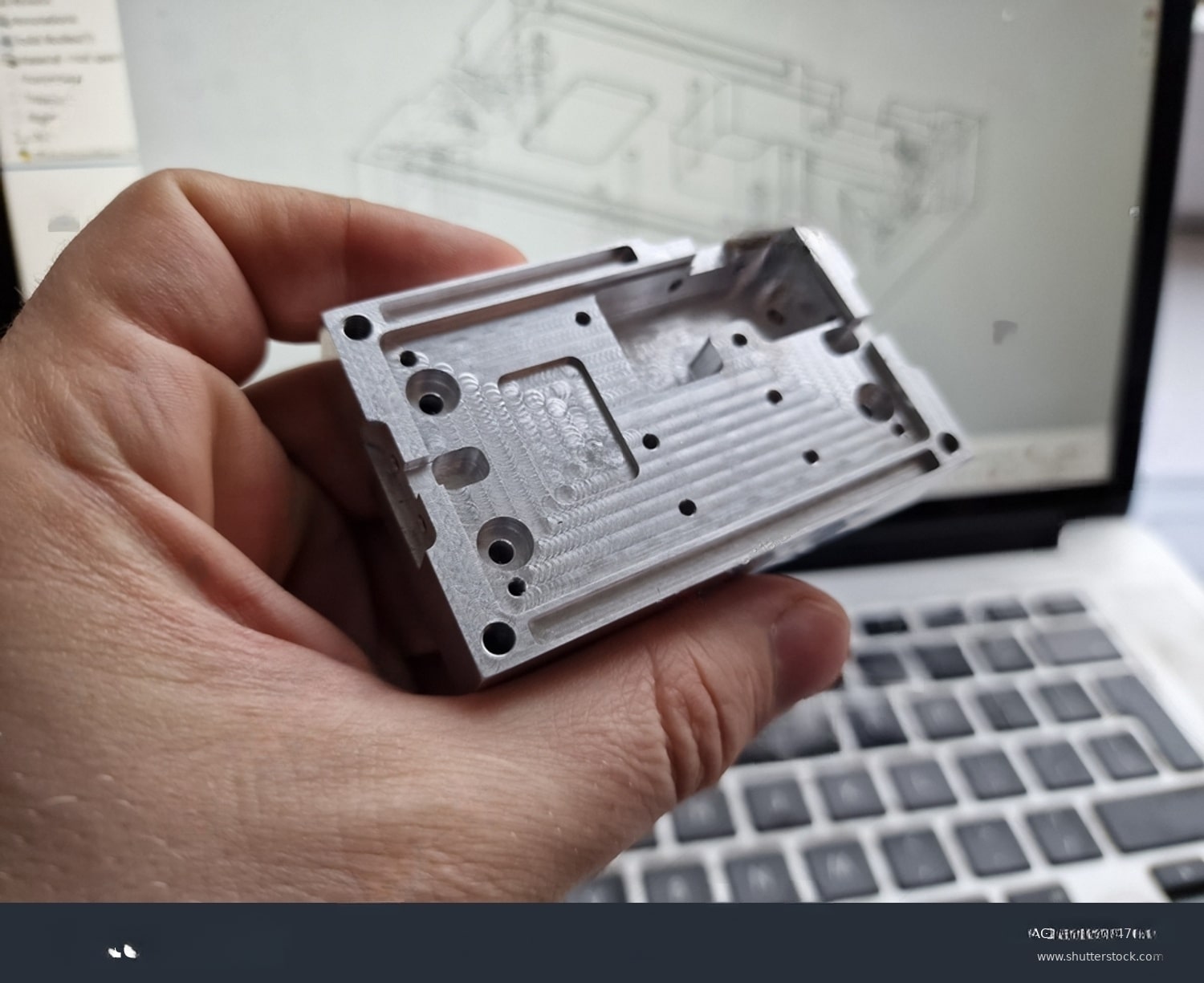

CNC milling is a computer-controlled subtractive manufacturing process that shapes materials with precision. It utilizes automated cutting tools in a milling machine to create intricately machined components accurately.
In CNC milling, a computer-controlled machine removes material from a workpiece to achieve the desired shape. It starts with a digital design created using CAD software and translated into machine instructions with CAM software. These instructions guide the milling machine to cut and shape the material precisely as per the design.
Multi-axis capability for simultaneous machining from multiple angles, reducing the need for multiple setups and ensuring superior accuracy and efficiency.
Customized tooling solutions tailored to your needs. We design and develop custom tools optimized for your milling needs, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency
Efficient production capabilities and dedicated team enable us to offer short lead times, allowing you to accelerate your product development cycle and bring your ideas to market faster.
advanced inspection techniques, including (CMMs), to verify dimensional accuracy and conformance to specifications. we maintain comprehensive traceability records
| Tolerace | Standard/Feasible Tolerance Range |
|---|---|
| Linear | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm (±0.002 inches to ±0.008 inches) Allowable variation in dimensions along straight edges or lines |
| Angular | ±0.5° to ±2° Allowable deviation from a specified angle. It is typically used for features with angular requirements, such as chamfers or draft angles. |
| Positional | ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm (±0.004 inches to ±0.020 inches) Controls the location of features relative to a datum. It ensures the precise positioning of holes, slots, or other critical features. |
| Diameter | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm (±0.002 inches to ±0.008 inches) Permissible variation in the size of circular features, such as holes or bores. |
| Concentricity | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm (±0.002 inches to ±0.008 inches) Permissible offset between the centers of two concentric features, such as a shaft and its mating hole. |
Aluminum is a versatile and widely used material in CNC machined components manufacturing. It is a lightweight metal with a density of approximately 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), making it about one-third the weight of steel. Despite its low density, aluminum exhibits remarkable strength, especially when alloyed with elements such as copper, magnesium, or zinc.

CCC, Anodizing, Media Blasting, Nickel Plating, Powder Coating, Tumbling, Polishing.
Steel is the most commonly used material in CNC machining, renowned for its strength, versatility, and durability. Steel can vary in composition, resulting in a range of grades with distinct characteristics. Steel offers exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, which can range from around 300 to 2,000 (MPa), depending on the grade. Its hardness can also be tailored through heat treatment processes. Steel’s excellent machinability allows for precise shaping and fabrication during CNC machining operations.

Low Carbon Steel (AISI 1018)/C15E(1.1141)
Medium Carbon Steel (AISI 1045)/C45E(1.1191)
High Carbon Steel (AISI 1095)/C100S(1.1274)
AISI 4140/42CrMo4 (1.7225) | AISI 4340/34CrNiMo6 (1.6582)
AISI 8620/20NiCrMo2-2 (1.6523)
ASTM A36 / ASTM A105 / ASTM A516
S235JR(1.0038) / S355JR(1.0045)
Black Oxide, Electropolishing, Media Blasting, Nickel Plating, Powder Coating, Tumbling, Polishing, Zinc Plating,
CNC machinists appreciate stainless steel for its machinability and the precise results it offers during manufacturing processes. With its aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and suitability for diverse applications, stainless steel remains a top material for CNC machining. Its sleek and modern appearance makes it a popular choice for various applications.

Austenitic
304 (1.4301, X5CrNi18-10) | 304L (1.4307, X2CrNi18-9)
316 (1.4401, X5CrNiMo17-12-2) | 316L (1.4404, X2CrNiMo17-12-2)
Ferritic
430 (1.4016, X6Cr17)
Martensitic
410 (1.4006, X12Cr13) | 420 (1.4021, X20Cr13) |416 | 1.4005 | X12CrS13
Duplex
2205 (1.4462, X2CrNiMoN 22-5-3) | 2507 (1.4410, X2CrNiMoN 25-7-4)
Precipitation-hardening
17-4PH (1.4542, X5CrNiCuNb16-4) | 15-5PH (1.4545, X5CrNiCu15-5)
Superaustenitic
904L (1.4539, X1NiCrMoCu25-20-5) | 254SMO (1.4547, X1CrNiMoCuN20-18-7)
Silver
Black Oxide, Electropolishing, Media Blasting, Nickel Plating, Passivation, Powder Coating, Polishing, Zinc Plating, Tumbling(Vibratory)
Tool steel exhibits excellent dimensional stability and resistance to deformation, allowing it to maintain its shape and cutting edge under demanding machining conditions. Its high wear resistance ensures longevity and efficient machining performance. Tool steel’s exceptional heat resistance enables it to withstand elevated temperatures generated during CNC machining operation

AISI D2 (DIN 1.2379)/AISI O1 (DIN 1.2510)/AISI A2 (DIN 1.2363)
AISI S7 (DIN 1.2355)/AISI H13 (DIN 1.2344)/AISI M2 (DIN 1.3343)
AISI M42 (DIN 1.3247)/AISI T1 (DIN 1.3355)AISI D3 (DIN 1.2080)
AISI H11 (DIN 1.2343)/ISI L6 (DIN 1.2714)AISI P20 (DIN 1.2311)
Metallic Grey
Media Blasting, Black Oxide, Powdercoating, Vibratory Tumbling
Cast iron is an alloy of iron, carbon, and other elements, such as silicon and manganese. Its known for its exceptional strength, hardness, and wear resistance, making it suitable for applications that require durability and high load-bearing capacity. Due to its excellent vibration damping properties, cast iron is suitable for components that require reduced noise and vibration levels.

Gray Iron: ASTM A48, A126 / EN-GJL
Ductile Iron: ASTM A536 / EN-GJS
Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI): ASTM A842 / EN-GJV
Malleable Iron: ASTM A47 / EN-GJM
White Iron: ASTM A532 / EN-GJMW
Dull gray, Silver-gray
Tumbling, Media Blasting
Brass is a widely used material in CNC machining due to its excellent combination of properties. It is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, with varying compositions depending on the desired characteristics. In terms of mechanical properties, brass offers good strength, malleability, and ductility. Its machinability is another advantage, as brass can be easily formed, cut, and shaped during CNC machining processes.

Media Blasting, Polishing. Brushing
Copper is an ideal choice for applications that require efficient heat transfer or electrical conduction. With a density of approximately 8.96 (g/cm³), copper is relatively dense. Copper possesses good tensile strength and is highly malleable and ductile. It exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in atmospheric and marine environments. These properties, along with its antimicrobial qualities, make copper suitable for various CNC machining applications.
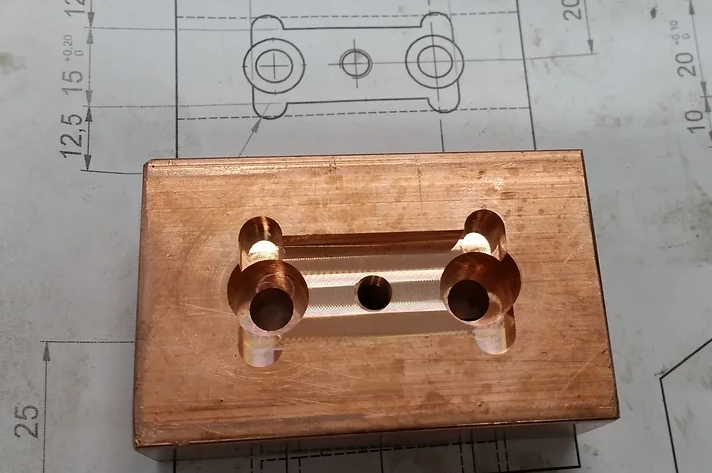
As machined, media blasting, polishing.
Titanium is a sought-after material for cnc machining due to its strength and high ductility, allowing for intricate designs. It is a lightweight metal with a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, weighing about 45% less than steel while maintaining similar strength. It also offers excellent corrosion resistance, even in harsh environments, and is resistant to erosion and fatigue. Titanium’s high melting point of around 1,670°C (3,038°F) makes it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Titanium Grade 1/CP-Ti (Pure Titanium)
Titanium Grade 2/CP-Ti (Pure Titanium)
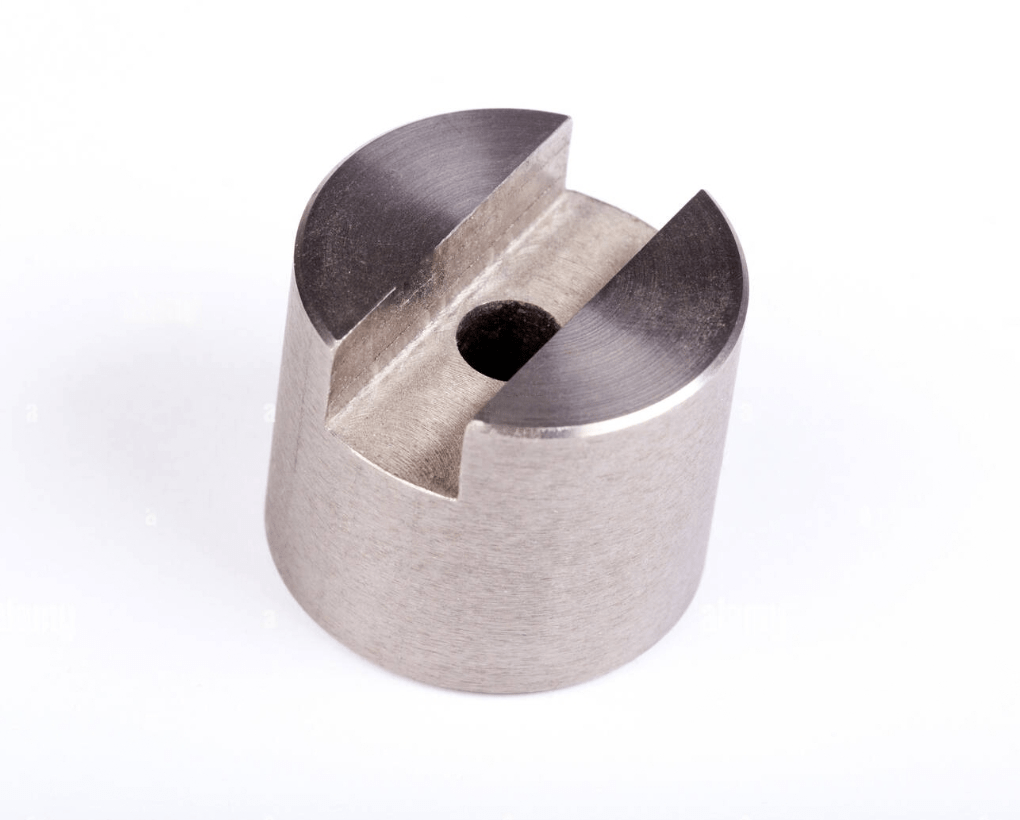
Grade 5/Ti-6Al-4V
Grade 6/Ti 5Al-2.5Sn
Grade 9/Ti-3Al-2.5V
Grade 12/Ti 3Al 2.5
Media Blasting, Vibratory Tumbling, Passivation, Powder coating
Nickel alloys, such as Inconel and Monel, exhibit exceptional strength, toughness, and resistance to extreme temperatures, making them ideal for demanding CNC machining applications, like aerospace components, marine equipment, chemical processing equipment, and high-temperature applications. Nickel can be machined using various CNC techniques, including milling, turning, and drilling, allowing for the creation of precise and complex parts with excellent dimensional stability.

Inconel 600 (UNS N06600)
Inconel 625 (UNS N06625)
Inconel 718 (UNS N07718)
Inconel 825 (UNS N08825)
Invar 36 (UNS K93600)
Kovar (UNS K94610)
Monel 400 (UNS N04400)
Monel K500 (UNS N05500)
Vibratory Tumbling, Media Blasting, Powdercoating
Magnesium is known for its low density, weighing in at approximately 1.74 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). This characteristic makes it one of the lightest metals employed in structural applications. Despite its feather-light nature, magnesium boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, which contributes to substantial weight reduction across a wide range of uses. For e.g. the AZ91D magnesium alloy, frequently used in CNC machining.

Media Blasting, Powder Coating, Vibratory Tumbling,
Zinc is highly malleable and ductile, allowing for easy shaping, bending, and forming during CNC machining. It also has good thermal and electrical conductivity. Zinc alloys, such as Zamak (a popular zinc alloy), offer enhanced properties and are widely used in CNC machining for various applications, including automotive components, electronic enclosures, decorative hardware, and plumbing fittings.
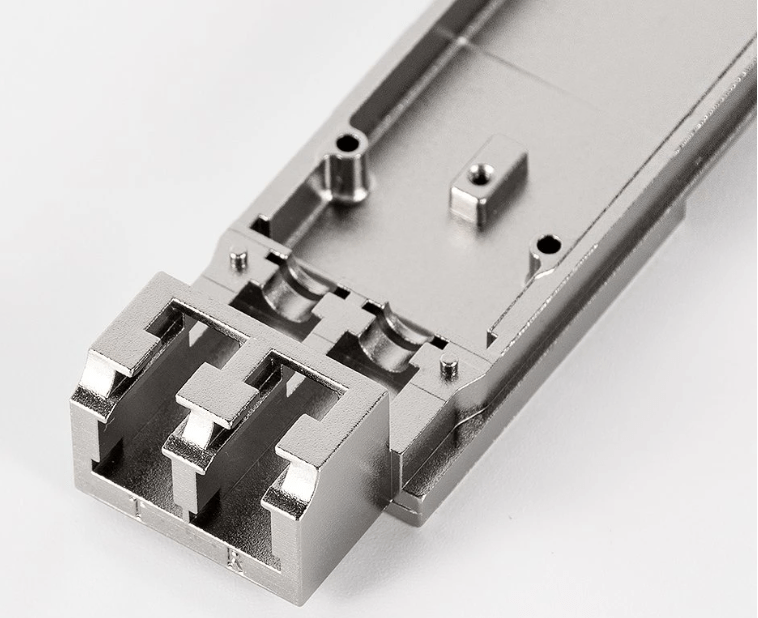
Media Blasting, Powder Coating, Tumbling
CNC milling plays a vital role in a wide range of industrial applications. One such area is the automotive industry, where CNC milling machines are used to manufacture engine components, chassis parts, and even customized prototypes.
The precision and efficiency of CNC milling enable the production of intricate parts with tight tolerances, ensuring optimal performance in vehicles.
CNC milling finds extensive application in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and prototyping. Its ability to deliver precision, efficiency, and versatility makes CNC milling an indispensable technology for manufacturing complex parts and components across diverse sectors.
CNC milling also finds extensive use in the aerospace sector, where complex aircraft parts with high accuracy requirements are produced.
From turbine blades to structural components, CNC milling machines deliver the precision and reliability needed for critical aerospace applications.
Another industry that heavily relies on CNC milling is the medical field. CNC milling machines are instrumental in manufacturing medical devices such as implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments.
The ability to work with various materials, including biocompatible metals and plastics, allows for the creation of customized medical solutions. CNC milling ensures precise dimensions and smooth finishes, guaranteeing compatibility and comfort for patients.

Green energy products of the highest class
Type | Applicable to | Machining marks | Color | Tolerances | Can be applied with | |
 | Anodizing | Aluminum, Titanium | Minimized for non cosmetic, removed on external surfaces for cosmetic | Wide range, customizable | Tolerances are not affected | Media Blasting, Tumbling, CCC* |
 | Black Oxide | Copper, Stainless steel, Alloy steel, Tool steel, Mild steel | Visible | Black | Met after coating | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Passivation |
 | Electroless Nickel Plating | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | Minimized but visible | Metallic | Met after plating | Media Blasting, Tumbling |
 | Electropolishing | Steel, Stainless Steel | Removed on external surfaces | N/A | Met after electropolishing | Always Passivation, Tumbling |
 | Media Blasting | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, Copper | Removed for non-cosmetic, removed on external surfaces for cosmetic | N/A | Tolerances are not affected | All post processes except Electropolishing and Powder coating |
 | Polishing | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, Bronze, Copper | Removed on external surfaces | N/A | Met after polishing | Used for cosmetic appearances |
 | Nickel Plating | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | Minimized for non cosmetic, removed on external surfaces for cosmetic | N/A | Met after plating | Media Blasting, Tumbling |
 | Passivation | Steel, Stainless Steel | Minimized but visible | N/A | Tolerances are not affected | Black Oxide, Electroless Nickel Plating, Zinc Plating, Tumbling, Media Blasting |
 | Powder Coating | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | Minimized for non cosmetic, removed on external surfaces for cosmetic | standard colors, metallic finishes | Normally met after Coating | Media Blasting, Tumbling |
 | Chromate conversion coating | Aluminum | Visible | Clear, gold | Tolerances are not affected | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Type II /Type III Anodizing*, Type III Anodizing with PTFE* |
 | Tumbling | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | Minimized but visible | standard colors, metallic finishes | Slightly affected after tumbling | All post processes except Electropolishing and Powder coating |
 | Zinc Plating | Steel, Stainless Steel | Minimized visibility on a substrate | Clear: light blue coating, black: glossy black coating | Met after plating | Media Blasting, Tumbling, Passivation |
Explore the essential Considerations and recommended Values for Optimal Machining operation for CNC Milling
| Features | Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | 2mm (for a specific part) |
| Fillets and Radii | 0.5mm (for a specific part) |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8-6.3 μm (depending on functional requirements and material) |
| Undercuts and Overhangs | Keep undercuts within 15°-30° range. |
| Pocket Design | Avoid deep pockets with high aspect ratios. |
| Parting Line and Part Orientation | Align parting line with primary features or simplify orientation. |
| Features for Fixturing | Design flat surfaces or slots for secure clamping. |
| Thread Design | Use standard thread sizes (e.g., M4, M6, etc.) |
| Internal Cavities | Provide access holes or milling ramps for efficient material removal. |
| Surface Protection | 0.2-0.5mm chamfer or radius on exposed edges. |
| Clearance and Interference | 0.1-0.3mm clearance for moving parts. |
| Part Markings | Engrave markings to a depth of 0.05-0.1mm. |
CNC milling offers numerous advantages over traditional manual milling methods. Some key benefits include
Increased Precision: CNC milling machines can achieve high levels of accuracy and repeatability, resulting in parts with tight tolerances.
Improved Efficiency: Automation eliminates the need for manual intervention, allowing for continuous production and reduced cycle times.
Enhanced Flexibility: CNC milling machines can handle complex geometries and perform multiple operations, reducing the need for multiple setups.
Cost-Effective: Once the machine is set up and programmed, CNC milling can be a cost-effective solution for large-scale production.
The spindle speed range in CNC milling machines can vary depending on the machine and the type of tool being used. Generally, spindle speeds can range from a few hundred RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) to several thousand RPM, allowing for optimal cutting speeds based on the material and tool diameter.
The maximum feed rate in CNC milling refers to the speed at which the cutting tool moves through the material during the milling process. The maximum feed rate can vary depending on the machine and the material being machined. It is typically measured in inches or millimeters per minute (IPM or mm/min) and can range from a few inches per minute to several hundred inches per minute.
CNC milling machines can perform various milling operations, including face milling, end milling, slot milling, drilling, and profiling. Face milling involves cutting across the surface of the workpiece to create a flat finish. End milling is used for cutting slots or pockets on the workpiece. Slot milling is the process of creating narrow slots in the workpiece. Drilling involves creating holes, and profiling is used to shape the workpiece according to a specific contour or profile.
CNC milling machines can achieve high levels of accuracy, typically within a few thousandths of an inch.
Yes, CNC milling is widely used for rapid prototyping due to its speed, accuracy, and ability to produce complex geometries.
CNC milling can be used with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and wood.